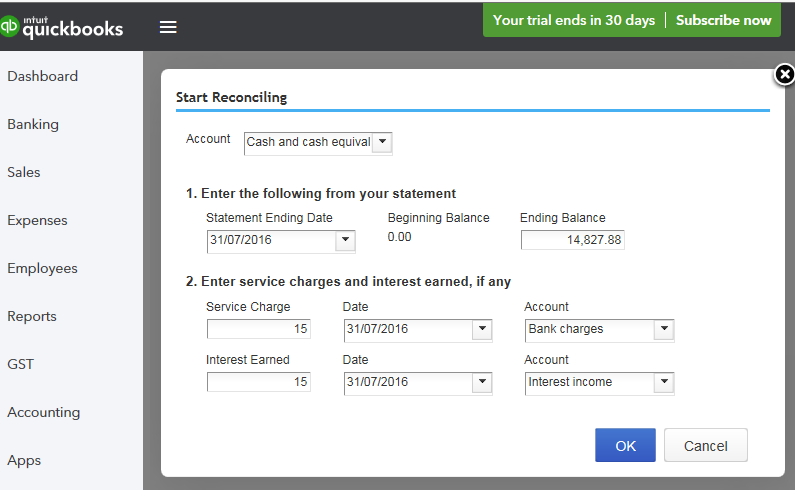
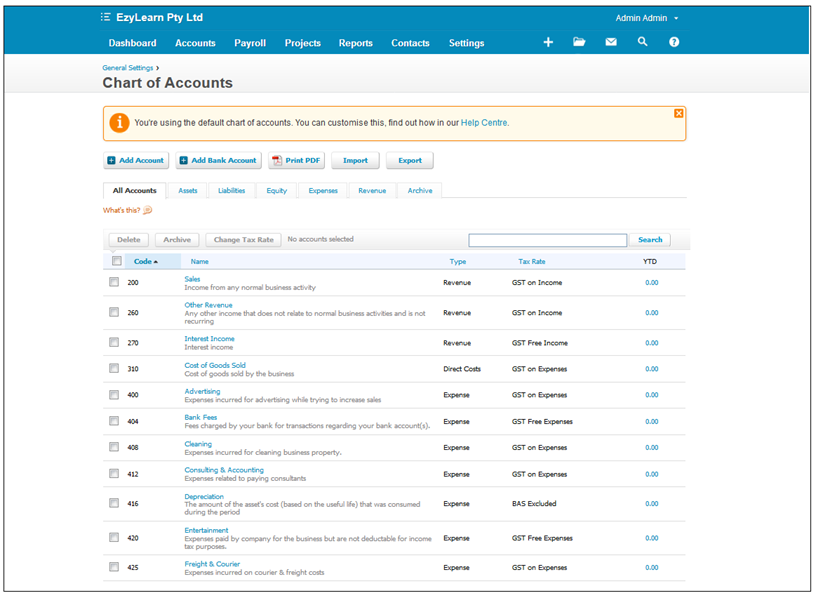
Bookkeeping Basics apply to every cloud accounting platform: MYOB, Xero or Quickbooks (QBO)

BOOKKEEPING IS THE PROCESS of keeping accurate records of the financial affairs of a business, and every business operating in Australia, whether it employs staff or whether it’s owned and operated by a single sole trader, must keep their bookkeeping up to date.
Bookkeeping plays a key role in the lodgement of your tax returns and business activity statements. It can also provide valuable information on the financial health and performance of your business.
The bookkeeping process for a business starts the very moment you begin trading, so it’s extremely important that you set up a system for managing your bookkeeping early in the life of your business — ideally, at the same time that you’re setting up your other operational systems (email accounts, websites, invoicing, etc). We’ve included bookkeeping basics videos in our MYOB training course for several years already but now these basics are part of a separate guide!

If you’ve never been self-employed before, just the idea of setting up a bookkeeping system is probably enough to strike fear in your heart, which is why we put together a free guide to setting up your own bookkeeping system, called Bookkeeping Basics, which you can download, for free, from the EzyLearn website.
The Bookkeeping Basics guide is an instruction manual on basic features and terminology used in every bookkeeping system, and will provide you with some good foundation knowledge of how your accounting software works, which you can use before you enrol in one of our cloud accounting training courses or find a good bookkeeper to take care of your bookkeeping for you.
Bookkeeping Basics Topic: Understanding cash vs. accrual accounting
The main difference between cash and accrual accounting is the timing of when when revenue and expenses are recognised. Although, the two methods are distinctly different from each other, there are many businesses that use a combination of both.
Cash-based accounting
A cash-based accounting system records transactions at the time the cash was paid or received, regardless of when the transaction occurred. With this method, if you get an invoice from a supplier, for instance, you won’t record the cost in your books until you’ve paid the invoice. By the same token, you won’t record a sale in your books until you receive the money from your customer.
Cash accounting is common among small businesses, especially contractors who work on small projects or are on weekly retainers with their clients, as it’s the simplest way to manage cash flow.
Accrual-based accounting
An accrual accounting system, on the other hand, recognises both income and expenses when the sale takes place, rather than when cash changes hands. When a web designer, for example, raises an invoice for a website they’ve completed, the sale would be recorded in their books, even though they haven’t received payment yet.
With accrual accounting, debtors and creditors are created in your accounting software, which shows what is owing to you and when, as well as what you owe others and when. This helps to give you a truer picture of your financial situation, in particular it helps you keep track of money you do and don’t have in real-time, rather than after the fact as is the case with cash-based accounting.
Which system should you use?
Before cloud accounting software, like MYOB, Xero and QuickBooks came along, a lot of small businesses used a cash-based accounting system simply because the alternative required a lot of grunt work, a lot of the time. Cloud accounting has made it significantly easier to set up and maintain an accrual-based accounting system — in fact, many small businesses that use a cloud accounting system often use this method by default, without even realising.
That being said, there are some things to consider when selecting a system for your business, such as:
- The size of your business — i.e., will you be employing staff or using lots of contractors?
- How complicated your business transactions will be
- Whether you will have the resources to manage an accrual system.
Accrual accounting and GST
There is one last thing to consider, and it relates to GST. For small businesses whose annual turnover is less than $2 million, but greater than $75,000 per annum, they must register for GST and they may choose whether or not to register on a cash or accrual basis. (Businesses with an annual turnover of less than $75,000 are not required to register for GST, but may do so if they wish to.)
How you choose to register for GST will greatly affect your business’s cash flow. If you choose to register for GST on an accrual basis, GST will be payable on sales for which payment hasn’t been received yet, and could leave you out of pocket until your client pays you. That being said, GST can be claimed on unpaid expenses if you hold a tax invoice. If your business has a lot of expenses, this may balance out in the wash. If you run a leaner operation, however, it most probably will not, so this is something you should give careful consideration to.
This blog post is part of our Bookkeeping Basics series, which are being published to complement our new educational guide, also titled Bookkeeping Basics, which you can download for free from the EzyLearn website.
[box type=”info”] This blog post is part of our Bookkeeping Basics series, which are being published to complement our new educational guide, also titled Bookkeeping Basics, which you can download for free from the EzyLearn website.[/box]
 If you’re looking for a reliable bookkeeper to manage your daily or weekly bookkeeping and accounts, either remotely or in-person, Deb from Mandurah WA is a qualified bookkeeper with tertiary qualifications and the practical experience of having operated her own business in the past. Deb has a lot of experience in the day-to-day accounting functions of a small business and you can contact her directly as a fully licensed member from her profile page.
If you’re looking for a reliable bookkeeper to manage your daily or weekly bookkeeping and accounts, either remotely or in-person, Deb from Mandurah WA is a qualified bookkeeper with tertiary qualifications and the practical experience of having operated her own business in the past. Deb has a lot of experience in the day-to-day accounting functions of a small business and you can contact her directly as a fully licensed member from her profile page.
Our National Bookkeeping website has recently gone through a significant upgrade so watch out for more stories about featured bookkeepers in forthcoming blogs! Join and we can feature YOU in our articles too.
Start a bookkeeping business in your local area
 Many bookkeepers starting a bookkeeping business for the first time also find it quite daunting; after all, they have moved from the corporate world where various and multifaceted aspects of running the business are managed by other people.
Many bookkeepers starting a bookkeeping business for the first time also find it quite daunting; after all, they have moved from the corporate world where various and multifaceted aspects of running the business are managed by other people.
We put these bookkeepers through our EzyStartUp Course to help them define their goals, pricing strategies, marketing message and professional profile. They also get support from a business mentor and brand building from our digital marketing team.